There are many types of fats out there and sometimes it can be difficult to know which ones we should avoid. While we know that omega fatty acids are good for us, there is more than one kind and not all have the desired effect on our body. In this article we will explain what omega – 6 fatty acids are and why their ratio to omega – 3 in our diet is so important.
What Is Omega – 6 And What Is The Difference To Omega – 3?
Omega – 3 and omega – 6 are so called polyunsaturated fatty acids. This refers to the molecular structure they have and means that they both have several double bonds in the molecule, which makes them a relatively stable compound. The number 3 and 6 refer to the location of the final double bond in the molecule. Omega – 3s have their final double bond in the 3rd carbon atom before the end, omega – 6 in the 6th, which is also the only difference in their structure. However, this change in configuration also signifies differences in their effect and function on and in our body. They are also both essential fatty acids, which means that our body is not able to produce them itself but that we need to consume them through our diet.
The most common and important omega – 3 for us are called eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). ALA comes from plant sources such as algae or flaxseeds and is mostly used for energy by our body. It can be converted into EPA and DHA in our system so it is usually considered the “original” omega – 3, however this process of converting ALA is very inefficient so it makes more sense for us to eat foods rich in EPA and DHA directly such as seafood for example.
DHA makes up 8% of our brain weight and is important for brain development and function. EPA on the other hand produces a chemical called eicosanoid which helps to reduce inflammation, EPA itself also helps to alleviate symptoms of depression.
There is a lot of research about the health benefits of omega – 3 because they have been considered a valuable food supplement for a long time and therefore have been studied extensively. Some more of its benefits are the impact on cell membranes, improvement of heart health and support of the immune system, to name just a few. Research has also shown that an omega – 3 deficiency can have negative impacts on us and can contribute to chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
The most commonly consumed omega – 6 is called linoleic acid (LA) and is mostly used for energy in our body. Like ALA, LA can be converted into another substance: arachidonic acid (AA).
But what is the impact of those omega – 6 fatty acids and are they healthy for us?
Is Omega – 6 Good Or Bad For Us?
AA, just like the omega – 3 EPA, can produce eicosanoids. However, some research suggests that those produced by AA are more pro-inflammatory in their effect than the ones produced by EPA. And while they play an important role in our immune system, an overproduction of eicosanoids could potentially have negative consequences and increase overall inflammation in our body as well as the risk for inflammatory diseases. Inflammation is an important protective mechanism of our immune system to fight off infections and protect us from potential injury, however if the inflammation becomes chronic or is present in an excessive intensity, it can cause damage to our body. This all might sound a bit technical and abstract, but inflammation is basically a main driver of common diseases such as arthritis, diabetes or heart disease.
To say however, that omega – 6 are flat out bad for us is too simplistic as well. They are essential for the proper working of our body and we do need them in our system. Also, the quantity of LA that gets converted into AA is quite small and like with ALA, the process is not very efficient either. Not all LA gets converted so we cannot automatically conclude that a high intake of LA signifies a high level of AA producing “bad” eicosanoids.
So what it comes down to, like with most things in life, is balance. We do need both omega – 3 and omega – 6, but not too much of the latter.
So how do we achieve a good balance and what ratio of omega – 3 and omega – 6 should we try to get through our diet?
It’s All About Balance – What Is A Good Omega – 3 to Omega – 6 Ratio?
So our diet has changed a lot throughout time and today many people have access to food from all over the world. However, especially the Western diet is out of balance when it comes to the way we consume fats. Not all fats are bad, but it is important that we eat enough of the “good” ones and not too many of the “bad” ones.
If we specifically look at the ratio between omega – 3 to omega – 6 there has been a strong shift towards more omega – 6 in our typical Western diet. Some scientists suggest, based on their knowledge of the impact of those fatty acids on inflammation levels, that this imbalance could have negative effects on our overall health. This could promote the onset of diseases such as cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disease and diabetes, which are strongly linked to chronic inflammation processes in our body.
We also know that omega – 3s have an anti-inflammatory effect, so ideally we should try to reduce our omega – 6 intake and increase our omega – 3 intake. With a higher intake of omega – 3 scientists are suggesting that we can reduce the risk of several chronic diseases that occur a lot in Western societies.
Most people consuming a regular Western diet have an omega – 6 to omega – 3 ratio from 10:1 to 50:1, but recommended is a 4:1 ratio. So how is it that we eat so many more omega – 6 than we should?
What To Eat – Foods That Contain A Lot Of Omega – 6
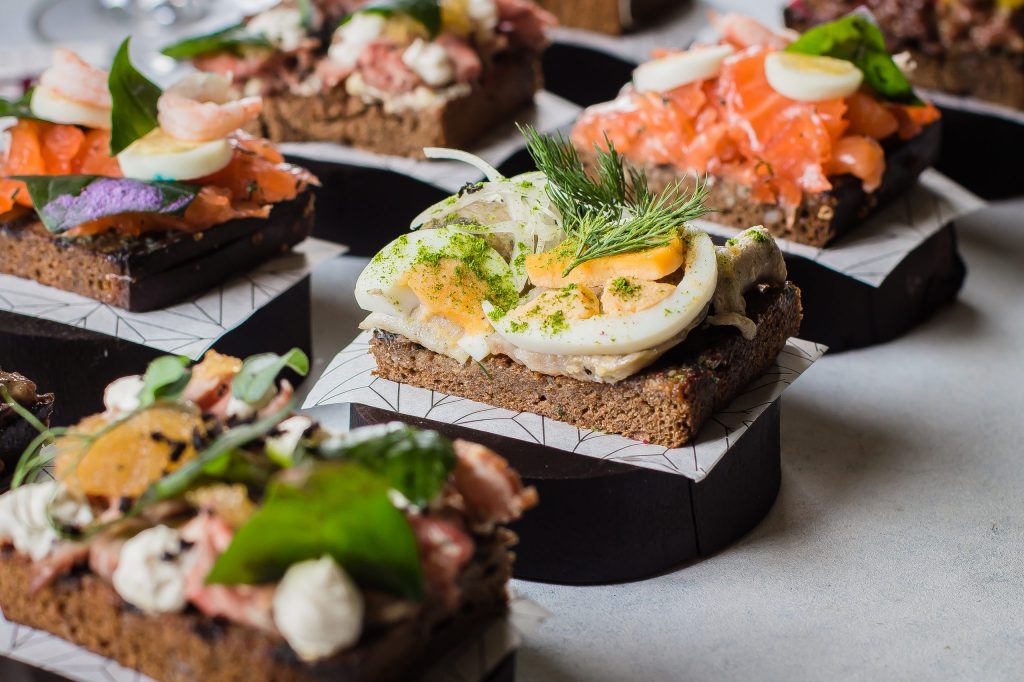
Surveys have shown that soybean oil is the biggest source of omega – 6 for Americans today. This is mainly because it is cheap and used in a lot of processed foods. Other foods that contain high amounts of omega – 6 are other vegetable oils like corn or sunflower oil and most processed foods that are made with these oils. To reduce our omega – 6 intake it would therefore be better to use butter, coconut oil or olive oil for cooking as those are lower in omega – 6. Besides decreasing our omega – 6 intake we should also try to increase the amount of omega – 3 we eat. The easiest way to do that is through seafood such as coldwater fish like salmon, which contain EPA and DHA, about twice a week. Since the transformation from ALA into EPA and DHA is not very efficient, it is better to consume them directly. If you want to know more about what foods contain abundant amounts of omega – 3, check out this (https://norwayomega.com/blog/which-products-provide-abundant-amounts-of-omega-3-fatty-acids/) blog post. There are also other diets that typically contain a lot of omega – 3 like the Nordic (https://norwayomega.com/blog/omega-3-the-nordic-diet/) or Mediterranean diet for example.
Another option is to take omega – 3 supplements such as fish oil or red krill oil. Those supply you with high doses of EPA and DHA and are linked to many health benefits such as better heart health and a stronger immune system.
Head over to our Shop to browse our range of products.
Source